Mengenal Hilirisasi Digital: Pengertian Hilirisasi Digital
Baca Juga: Internet of Things: Technology and Manufacturing Cultural Heritage
Hilirisasi digital telah menjadi buzzword di era digital ini. Ini bukan sekadar sebuah konsep, tapi lebih merupakan transformasi yang mengubah cara kita berinteraksi, bekerja, dan menjalankan bisnis. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan membahas secara mendalam tentang hilirisasi digital, apa dampaknya, serta bagaimana kita bisa memanfaatkannya untuk menghadapi tantangan masa depan.
Apa Itu Hilirisasi Digital?
Hilirisasi digital adalah proses transformasi bisnis, ekonomi, dan sosial yang didorong oleh teknologi digital. Ini melibatkan integrasi teknologi informasi dan komunikasi (TIK) dalam berbagai aspek kehidupan sehari-hari, mulai dari produksi hingga distribusi, pemasaran, dan konsumsi barang dan jasa. Dalam konteks ini, hilirisasi merujuk pada peningkatan nilai tambah, efisiensi, dan inovasi yang dihasilkan dari penerapan teknologi digital.
Dampak Hilirisasi Digital
- Peningkatan Efisiensi: Dengan memanfaatkan teknologi digital, proses produksi dan distribusi dapat dipercepat dan disesuaikan dengan kebutuhan pasar secara real-time. Ini menghasilkan efisiensi yang lebih besar dalam rantai pasokan dan manajemen inventaris.
- Pengembangan Inovasi: Hilirisasi digital memungkinkan perusahaan untuk mengembangkan produk dan layanan baru yang didukung oleh teknologi canggih seperti kecerdasan buatan (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), dan komputasi awan. Ini membuka peluang baru untuk menciptakan nilai tambah dan diferensiasi di pasar.
- Peningkatan Akses: Teknologi digital juga memungkinkan akses yang lebih luas terhadap informasi, produk, dan layanan. Ini dapat meningkatkan inklusivitas ekonomi dengan memungkinkan partisipasi lebih banyak orang dalam ekonomi digital.
- Transformasi Model Bisnis: Hilirisasi digital seringkali memaksa perubahan dalam model bisnis tradisional. Contohnya adalah peralihan dari penjualan langsung ke konsumen (B2C) menjadi model bisnis berbasis platform atau langganan (subscription-based).
Strategi Menghadapi Hilirisasi Digital
- Adopsi Teknologi: Perusahaan perlu secara proaktif mengadopsi teknologi digital yang relevan dengan bisnis mereka. Ini termasuk investasi dalam infrastruktur TI yang memadai dan pelatihan karyawan dalam penggunaan teknologi baru.
- Pengembangan Kapasitas: Hilirisasi digital membutuhkan keterampilan dan pengetahuan yang baru. Perusahaan perlu mengembangkan kapasitas internal mereka melalui pelatihan dan pengembangan karyawan agar dapat mengikuti perkembangan teknologi.
- Kolaborasi Industri: Kerjasama antara perusahaan, pemerintah, dan lembaga akademis dapat mempercepat hilirisasi digital dengan memfasilitasi pertukaran pengetahuan, sumber daya, dan peluang bisnis.
- Fokus pada Pengalaman Pengguna: Dalam menghadapi hilirisasi digital, perusahaan harus tetap berfokus pada pengalaman pengguna yang menyeluruh. Ini meliputi desain produk dan layanan yang intuitif, responsif, dan berorientasi pada kebutuhan pengguna.
Kesimpulan
Hilirisasi digital telah menjadi pendorong utama perubahan dalam ekonomi global. Perusahaan yang berhasil mengadopsi dan mengintegrasikan teknologi digital dalam operasi mereka akan memiliki keunggulan kompetitif yang signifikan. Namun, untuk mencapai hal itu, diperlukan komitmen yang kuat, investasi yang bijaksana, dan kemampuan untuk beradaptasi dengan cepat terhadap perubahan teknologi dan pasar. Dengan memahami esensi dan implikasi hilirisasi digital, perusahaan dapat mengubah tantangan menjadi peluang dan meraih kesuksesan dalam era digital ini.
Manfaat IoT untuk Bisnis

Baca Juga: Manfaat IoT Di Berbagai Bidang
Internet of Things (IoT) telah membawa revolusi dalam dunia bisnis dengan mengubah cara perusahaan beroperasi dan berinovasi. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan menjelajahi lima manfaat utama Internet of Things untuk bisnis, menggali lebih dalam bagaimana teknologi ini dapat meningkatkan efisiensi, produktivitas, dan menciptakan keunggulan kompetitif.
1. Peningkatan Efisiensi Operasional

Baca Juga: Transformasi Digital Sukses dengan Peran AI: Keunggulan Kecerdasan Buatan dalam Bisnis Anda
Dengan penerapan IoT, perusahaan dapat mengoptimalkan proses operasional mereka. Sensor-sensor yang terhubung secara cerdas memungkinkan pemantauan real-time terhadap berbagai elemen, seperti suhu, kelembaban, dan kecepatan mesin. Sebagai hasilnya, pengelolaan rantai pasok menjadi lebih efisien, persediaan dapat diukur dengan akurat, dan keputusan dapat diambil berdasarkan data yang akurat.
2. Inovasi Produk dan Layanan

Baca Juga: Transformasikan Bisnis Anda dengan Solusi IoT dari Nocola: Temukan Partner Digital yang Tepat!
IoT memungkinkan perusahaan untuk mengembangkan produk dan layanan yang lebih cerdas dan terkoneksi. Dengan menyematkan sensor ke dalam produk, perusahaan dapat mengumpulkan data konsumen untuk memahami perilaku pengguna dan meningkatkan pengalaman pelanggan. Contohnya, perusahaan mobil dapat menyediakan layanan pemeliharaan yang dipersonalisasi berdasarkan data kondisi mobil yang dikirimkan oleh sensor.
3. Analisis Data yang Mendalam

Baca Juga: Apa sebenarnya Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT)? Klarifikasi dan 5 Keunggulan Bisnis
IoT menghasilkan jumlah data yang besar, dan dengan analisis data yang canggih, perusahaan dapat menggali wawasan mendalam. Pemahaman yang lebih baik tentang perilaku pelanggan, tren pasar, dan kinerja produk dapat membantu perusahaan membuat keputusan yang lebih baik. Analisis data yang mendalam juga membantu dalam merancang strategi pemasaran yang lebih tepat sasaran.
4. Peningkatan Keamanan

Baca Juga: 5 Aplikasi Machine Learning yang Seru di Bisnis
Dengan meningkatnya serangan siber dan risiko keamanan, IoT memberikan solusi untuk melindungi data bisnis. Sensor keamanan dan enkripsi data memastikan bahwa informasi sensitif terlindungi. Selain itu, sistem IoT dapat memberikan peringatan dini terhadap potensi ancaman keamanan, memungkinkan perusahaan untuk mengambil tindakan sebelum terjadi kerusakan yang signifikan.
5. Penghematan Biaya

Baca Juga: Layanan IoT dan Extra Service Nocola yang Akan Mentransformasi Bisnis Anda
Meskipun investasi awal yang diperlukan untuk menerapkan teknologi IoT, jangka panjangnya dapat menghasilkan penghematan biaya yang signifikan. Dengan memantau dan mengelola aset secara efisien, perusahaan dapat mengurangi biaya perawatan dan pemeliharaan. Penggunaan energi yang lebih efisien juga dapat mengurangi biaya operasional.
Kesimpulan
Dengan mengadopsi Internet of Things, perusahaan dapat mengambil langkah besar menuju transformasi digital. Dari peningkatan efisiensi operasional hingga inovasi produk dan layanan, IoT membuka peluang baru bagi bisnis untuk mencapai keunggulan kompetitif. Penting bagi perusahaan untuk merencanakan dan mengimplementasikan strategi IoT yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan mereka untuk meraih manfaat penuh dari teknologi ini. Sebagai pelaku bisnis, tidak hanya penting untuk mengikuti tren, tetapi juga untuk memimpin dan menciptakan peluang baru melalui integrasi IoT dalam strategi bisnis mereka.
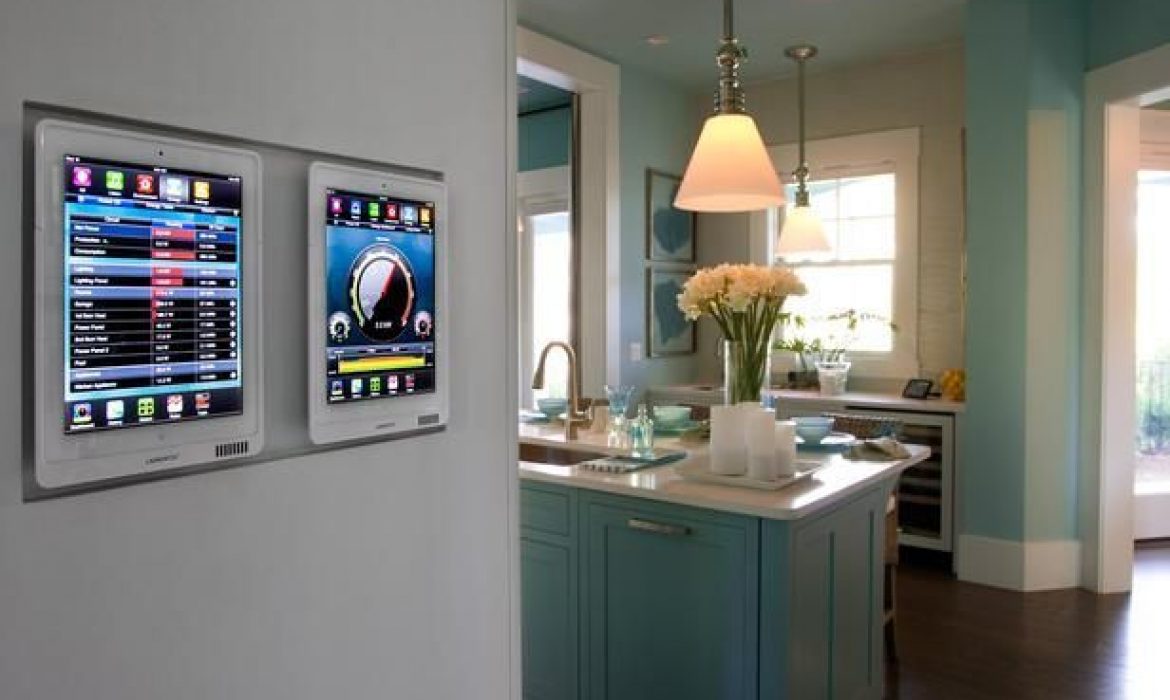
Smart Home IOT yang Sering Digunakan
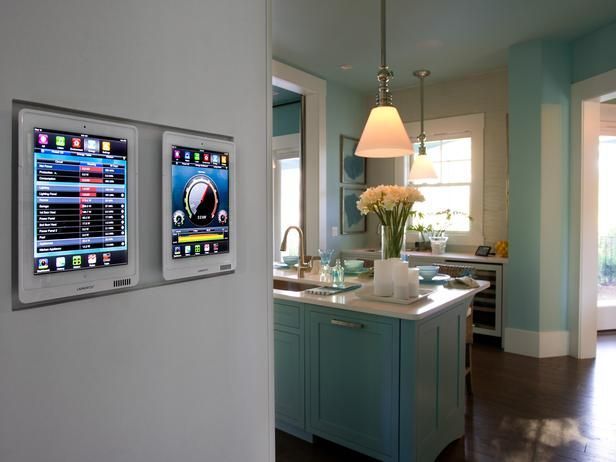

Baca Juga: IoT Smart Parking dengan Slot Monitoring di IPC
Dalam era digital ini, Internet of Things (IoT) telah mengubah cara kita menjalani kehidupan sehari-hari. Salah satu bidang yang mendapatkan dampak besar adalah smart home, di mana perangkat-perangkat pintar terkoneksi internet meningkatkan efisiensi dan kenyamanan di rumah. Dalam artikel ini, kita akan membahas tujuh smart home IoT yang sering digunakan, memberikan pandangan mendalam tentang bagaimana teknologi ini mengubah cara kita berinteraksi dengan lingkungan rumah.
1. Pintu Otomatis yang Terhubung ke Internet (Smart Locks)

Baca Juga: Membangun Kota Cerdas : 8 Hal yang Harus Dilakukan dengan Benar
Pintu otomatis yang terhubung ke internet atau smart locks merupakan salah satu inovasi terkemuka dalam industri smart home. Dengan menggunakan teknologi keamanan tinggi, smart locks memungkinkan pengguna untuk mengontrol akses pintu rumah mereka melalui smartphone atau perangkat terhubung lainnya.
2. Thermostat Cerdas (Smart Thermostats)

Baca Juga: 6 Aplikasi IoT Kesehatan untuk Rumah Sakit Pintar
Smart thermostats menjadi solusi terbaik untuk meningkatkan efisiensi energi di rumah. Dengan kemampuan untuk belajar pola penggunaan dan mengoptimalkan suhu secara otomatis, perangkat ini tidak hanya mengurangi tagihan listrik tetapi juga mendukung upaya pelestarian lingkungan.
3. Sistem Pemantau Keamanan Cerdas (Smart Security Systems)
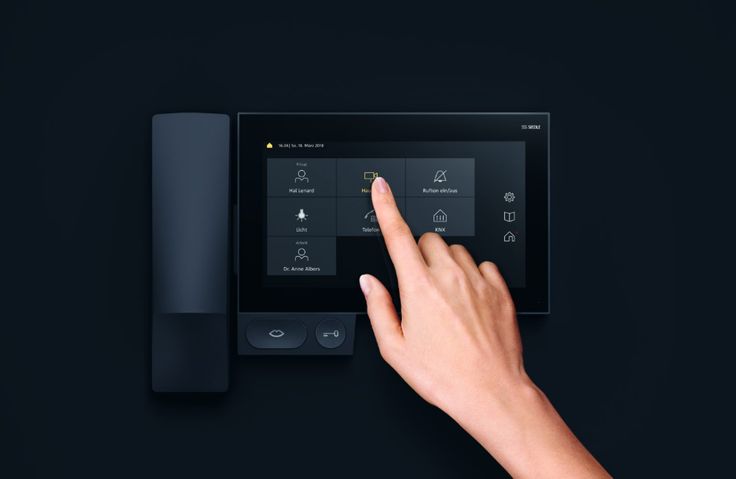

Baca Juga: Dasar-dasar Smart Building
Keamanan rumah menjadi prioritas utama, dan smart security systems menawarkan solusi canggih untuk melindungi rumah Anda.
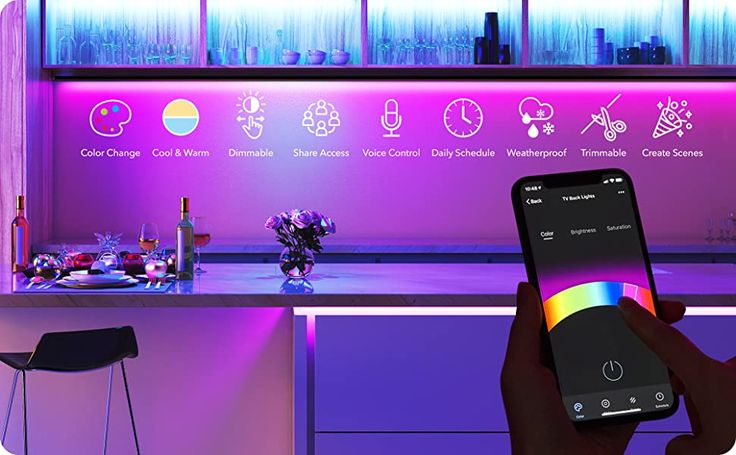
4. Lampu Pintar (Smart Lighting)
Baca Juga: Cara Mengatasi Virus Ransomware
Smart lighting memberikan kontrol yang lebih besar terhadap pencahayaan di rumah. Dengan kemampuan untuk disesuaikan dengan suasana hati atau bahkan diatur untuk mengikuti pola alami cahaya matahari, lampu pintar membawa efisiensi dan kenyamanan.
5. Speaker Cerdas (Smart Speakers)
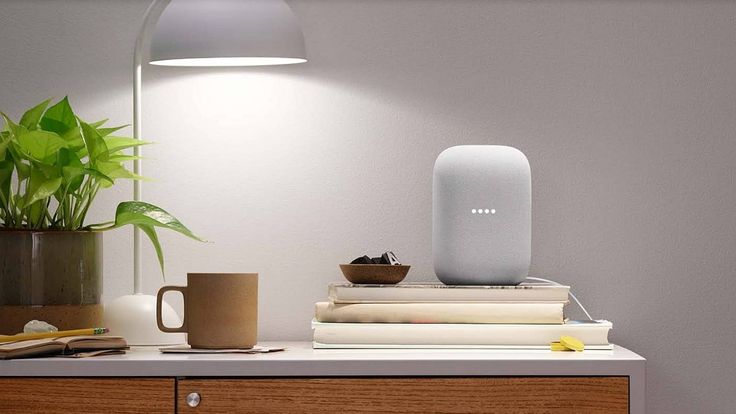

Baca Juga: Memahami Perbedaan: M2M vs IoT
Speaker cerdas seperti Amazon Echo atau Google Home tidak hanya berfungsi sebagai pemutar musik. Mereka menjadi pusat kontrol untuk berbagai perangkat pintar di rumah.
6. Mesin Cuci dan Pengering Pintar (Smart Washing Machines and Dryers)
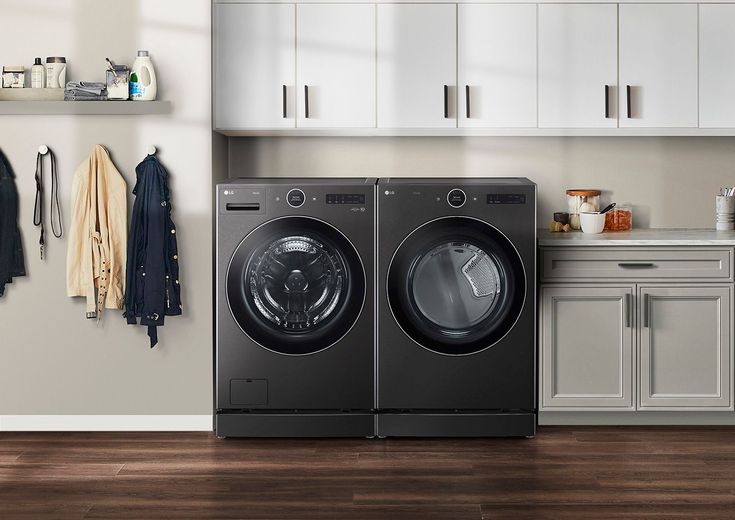

Baca Juga: Menuju Era IoT: 9 Contoh IoT yang Merevolusi Dunia
Dalam lingkungan smart home, mesin cuci dan pengering pintar menawarkan lebih dari sekadar mencuci dan mengeringkan pakaian. Mereka dapat diatur melalui aplikasi, memberikan pembaruan status, dan bahkan mempelajari preferensi pengguna.
7. Kunci Pintar untuk Kendaraan (Smart Car Keys)
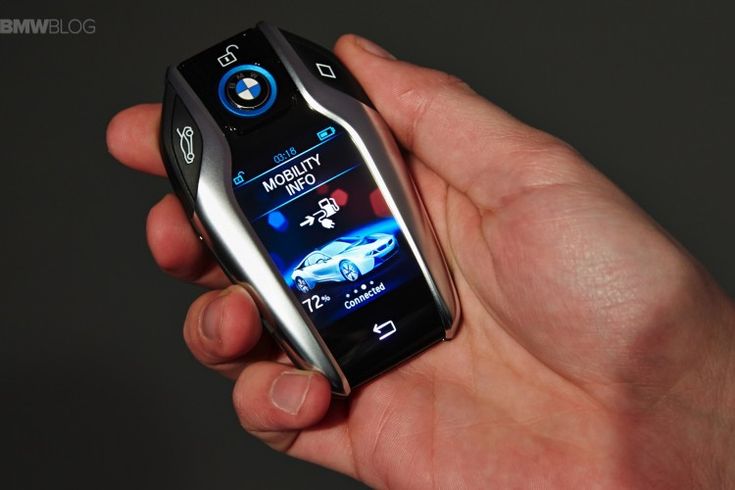

Baca Juga: Dasar-dasar Smart Building
Kunci pintar untuk kendaraan menjadi semakin populer, memungkinkan pengguna untuk mengontrol mobil mereka melalui smartphone.
Kesimpulan
Smart home IoT telah menjadi bagian integral dari kehidupan modern, memberikan solusi cerdas untuk meningkatkan kenyamanan, keamanan, dan efisiensi energi di rumah. Dengan berbagai perangkat pintar yang tersedia, pemilik rumah dapat menciptakan lingkungan yang lebih terhubung dan responsif. Penting bagi kita untuk terus mengikuti perkembangan teknologi ini untuk memanfaatkan inovasi terbaru dan menjadikan rumah sebagai tempat yang lebih cerdas dan nyaman.


